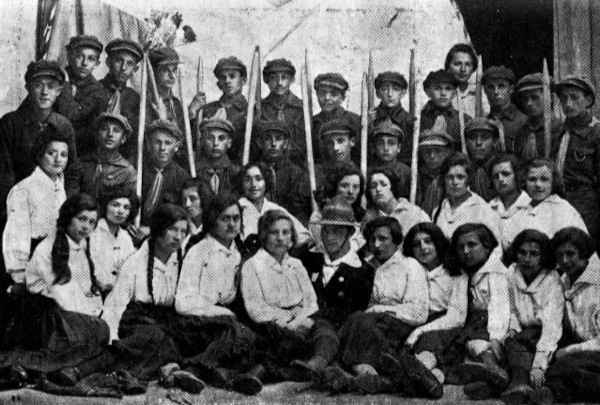
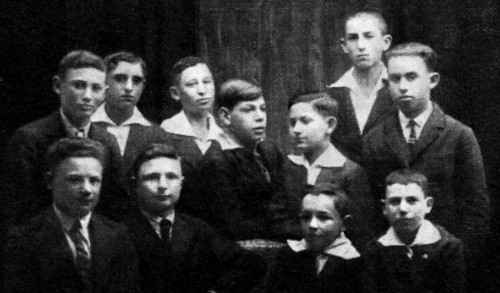[Page 217]
The “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir”[1] Center in Korets,
In Its Life and In Its Death
by Moshe Smolier
Translated by Monica Devens
The Great Revolution Among the Youth
The Jewish youth movement throughout Poland, whose path and development no one foresaw, came to Korets, too. The same motivations that set the existence of this movement in motion, the same sources from which the movement as a whole took sustenance, operated in the Jewish settlement in our city, too.
It was an expression of the revolt of the children and their struggle to change the shape of their lives. Revolt against the old, against what existed, whose motto was: “Don't listen, my son, to the father's principles and don't give ear to the mother's doctrine,” of the poet, David Shimonowitz. This was only part of the great motivation that, together with many other factors, stirred up the souls of Jewish youth and brought them to the movement.
Nevertheless, what was characteristic of this movement expressed itself principally in that, more than it rejected the past, it needed something new - the future.
World War I, with all of its ugliness, changed foundations and world views in the areas of principles, the family, and society. Jewish youth, having had bitter experience from the first steps of the 20th century, sought a way and an expression for itself and justification for its existence. In the depths of history, the saturation of blood and tears of our unfortunate people, never did the last spark die out - the belief that a day would come and this ancient and full-of-agony people would rejuvenate.
Freedom movements of downtrodden peoples in the world added to the breakthrough of the Jewish wall and, with the creation of the first cracks, powerful forces were let loose that destroyed every fence and boundary in their path. To the forest, to nature, to the field (and not just on Lag Ba-Omer), straighten one's back, strengthen one's muscles, toughen one's nature, and join the builders of the homeland - these slogans conquered the heart of the youth and built the movement.
The movement was carried, thus, on the wings of the revolt and was a faithful expression of the spirit of the times and of the desires of the souls of Jewish youth, and of that of Korets with it.
The organizers, founders, and bearers of this movement in our city were two members whose essence, character, and mentality typified the movement. They were Zev Czudner and Yitzhak Mezhyrichski.
Zev Czudner (brother of the poet, Czudner), a young Jew, with a warm
[Page 218]
Jewish soul, good observer and excellent guide, a wise and smart man, with a strong character, suited to the task of youth guide in a broad sense - had much organizational ability.
Yitzhak Mezhyrichski, a man with a European education, with broad principles, a gentle soul, a man who did not find improvement in the October Revolution - through many searches and much indecision came to the movement and became its head.
These two established the first youth movement in our city - “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir.” They also put their stamp on its direction, its character, and its development.
This typical Volhynian city did its duty towards good Zionist youth, lovers of their people, and full of longing for the yearned-for homeland. The youth of Korets were educated principally in accordance with the tradition. The large “Yeshiva” that stood out on “Shulgasse” [=Synagogue Alley] dominated not just the many synagogues in the city, but also shone on the souls of the youth and put its stamp on them. The surroundings, the Cheder, and the traditional education at home created a sort of spiritual whole.
This spiritual world was undermined by the difficult and ugly reality at the beginning of the third decade of the 20th century. The lack of any chance in the area of economic life, on the one hand, and the new spiritual pressure that was carried on the wings of the time, on the other, shook the foundations on which the structure was based. The youth of Korets burst forth from the ruins of this spiritual world, straightened their backs, and stood by the flag that was raised by the leaders of the “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” movement in the city.
In a short time, hundreds of youth congregated in the heart of the movement. The Kortchek River that divided the city into two sections and flowed peacefully on its never-ending way - was amazed more than once to hear Hebrew singing splitting the heavens. The footsteps of the groups and regiments, members of “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir,” heralded the changing times. Its calm waves welcomed the marching youth, it seemed, and forgave them for the quiet that was disturbed.
The heart rejoiced to see them marching with head held high, each under his flag. The place that the regiments and groups gathered was very symbolic. The two high mountains, through whose ravines the quiet river curved, hugged the surroundings with its strong arms and seemingly protected this young creation taking its first steps. The many paths that led the hundreds of youth, in a steep downhill to the mouth of the river, to a gathering of the like-minded, put this group on track.
The echo of the mountains to the greeting of the like-minded created wholeness of the animate and the inanimate, and the souls of the youth were lifted upward.
[Page 219]
|
|
The “Reuven” Group of “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir”Standing from right to left: 1) Chaim Fiszer, 2) Simon Finklesteinm 3) Gena Stambulchik, 4) Michael Schenker, 5) Freydes (Simcha's brother), 6)
Standing from right to left: 1) , 2) Moshe Smolier, 3) Yehoshua Basyuk, 4) Nachum Waserszturm, 5) Yitzhak Breindes, 6) Simcha Baraz, 7) Noach Garber, 8) Yitzhak Baraz, 9) Yitzhak Linik
Sitting from right to left: 1) Shlomo Shikher, 2) Eliezer Basyuk, 3) Yitzhak Torknitsch, 4) Shlomo Ozerinsky, 5) , 6) Moshe Feldman, 7) Eli Garber, 8) Mordechai Torknitsch, 9) Chaim Poliwa, 10) Yosef Wachbroit
Lying below: Sitting in the middle: Head of the Regiment, Zev Czudner (in the brimmed hat) |
[Page 220]
The Center turned into a real school for physical education, character strengthening, and fortifying the spirit of the youth. There, the first efforts were made for the youth to acquire the Hebrew language; there, they broadened the scope of knowledge of the young. From the walls of the Center, the first Hebrew song burst into the open. Literary sentences, subjects of a cultural and social nature, filled its substance. Its flag, the flag of revolt, was raised by the Zionist action that changed in the Center to a daily commandment. The new spirit that beat in the hearts of the marching youth to greet a new world and a different tomorrow was invigorated in it.
It is interesting that this revolt did not touch the holy of holies of the youth of Korets - the family. The strong attack of the defiant son did not touch the deep roots of the family. The love and respect for parents was, it seems, in keeping with the change in the lives of the youth in this place. The new spirit that carried the miracle of rebellion, established and built the movement, arose, it seems, with the agreement of the parents.
I will not forget the meeting in the great synagogue in 1925 of the parents of the Center, in which the leaders of the Center, the members Czudner and Mezhyrichski, raised an obligatory continuing education program for the members of the Center and it was demanded of the parents to participate in the costs. There were dozens of parents at this meeting from whom the spirit of the movement was very far, standing in complete opposition to their social position, their world view, and their life's desires - and still they agreed and joined themselves to this campaign. This was one of the interesting paradoxes: the rebellion of the son with the secret agreement of the parents. The movement was carried on the storm of the times and did not destroy bridges in its path.
The Rift
The two leaders were not made of one material. They were different in their characters, their approaches to matters were different, and it's likely that they were also divided in their opinions and their world views. Differences of opinion about the direction of the movement, forms of the organization, and the leadership also caused a temporary rift in the Center. I won't err if I say that this rift was, to a not small degree, also the result of the jealousy of the authors. In a short time, the rift was wiped out and the movement returned to its proper path, united and unified.
The organizational form of the Center matured and it was divided into three basic levels: Kfirim, Tzofim, and Bogrim.
The Kfirim: 10 years old and up, school pupils and children of all of the classes, from different houses, of different backgrounds, found their joint framework in this level. The games
[Page 221]
|
|
“The Trumpeldor Brigade”
Standing from right to left: 1) Yosef Kligerman , 2) Mordechai Torknitsch, 3) Yitzhak Wilner, 4) Fishman, 5) Yosef Wachbroit, 6) Yaakov Serber, 7) Yeshaya Serota. 8) Moshe Smolier, 9) Yitzhak Baraz, 10) Yehiel Goldberg,11) Eliezer Basyuk, 12) Shimon Broder, 13) Nachum Waserszturm
Second row from right to left: 1) Pinchas Raznoshik, 2) Zvi Galon, 3) Shmuel Gilman,4) Leibl Vaynshelboim, 5) Moshe Litvak, 6) Moshe Feldman, 7) Yehoshua Basyuk, 8) Simcha Baraz, 9) Chana Gilman
Third row from right to left: 1) Chaya Spielberg, 2) Shprintze Awret, 3) Batya Gilman, 4) Czarna Vigman, 5) Dvora Garbasz, 6) Chedva Melamed, 7) Goldberg
Last row from right to left: 1) Manya Rozenszturm, 2) Chana Grinfeld, 3) Bunya Vashkovker, 4) Pessie Katz, 5) Kupershmid, 6) Brigade Head Zev Czudner, 7) Esther Awret, 8) Chana Rayzberg (Basyuk), 9) Leah Neiterman, 10) Zeltke Berman, 11) Chaya Weintuch |
[Page 222]
and the singing and the conversation made up the substance of their lives. The “good deed,” which obligated the Kfir every day to a hard test of life, taught him to be a useful person in society and to do good deeds. The games and the singing introduced new substance to the lives of the children, content that they did not find either at home or at school. It is no surprise that this level was one of the largest and the dream of every 10-year-old child was to get into the ranks of the movement.
The Tzofim: the Tzofim regiments mostly took on the name of Herzl. The groups and companies of the Tzofim occupied themselves with continuing education, study of the Hebrew language, sports, and scouting. Dozens of young people gathered in the regiments of the Tzofim and were, basically, the foundation for the establishment of the Center. The struggle with school over change and spirit fell also on this level: the struggle with the teachers over the right of the students to have more free time and greater understanding on their part; the struggle with the parents over the equality of the youth and their spiritual independence. This was the age of the first clash with harsh reality.
The regiments of the Tzofim served, too, at the head of the bridge bringing together youth who studied in the “Tarbut” school and those who studied in the Polish school. The Center became the link bridging the two. This regiment also carried out a kind of pioneering leap and organized a summer colony. This was truly a revolutionary act. Twenty-and-some young people went into the forest in the village of Vodnik, spent ten days there, and lived under semi-military rule.
Various questions disturbed the leaders of the level the night before the campaign. What would the parents say? How would the surroundings respond? What would the villagers say? Would they not try to attack the camp on one of the nights?
That was 32 years ago. Did that experiment not leave its mark in changing reality? These were the Tzofim reigments - among the best of the youth of Korets.
The Bogrim: students of the Polish gymnasium and of the “Tarbut” school. Boys and girls who were indeed not brought up in accordance with the movement, did not draw from its rich well, and did not enjoy the brightness of the spirit of the educational movement that was clearing a path for it and carving Jewish reality in stone. Overnight, the boys and girls appeared suddenly and moved about the camp like giants. Everyone who looked at these youths was affected by their physical strength, by their outward appearance, and by the new spirit that wafted from their ranks.
Through aspiration for change in the manner of their lives and social atmosphere, they overcame the obstacle of immigration and fulfillment.
[Page 223]
The First Immigrants
“We are going up to the land”… the sounds of this song shattered the quiet and ideal air that prevailed on the Rovno [=Rivne] road. Along the sides of the road, group after group marched with its flag. They went out to accompany, and to say goodbye to, their immigrating friends: Yitzhak Mezhyrichski and Abba Berman.
The regiments arrange themselves. The flag of the Center flies about the heads of the immigrants. The words of parting were short, but difficult. The heart cries. For what and why? Is it only for your parting with a true friend, guide, and director? Or perhaps there already was an unconscious, vague, and unseen feeling? A feeling that broke through the darkness of the future and saw the open abyss? It may be that, already then, the heart prophesied the tragic future and created the feeling that they are seeing their friends for the last time. It is difficult to specify the reasons. The heart lamented and cried. The flag was raised and the sounds of “Techezakna” [=the Labor Zionist movement anthem] ended the parting. Yes, we parted, among them hundreds who did not have the privilege any more of seeing each other. The immigration road was the meeting place of hundreds of members, friends, and relatives, whom the flag united and fate separated for eternity …
The New Administration and the Turning Point
With the beginning of immigration, the activist team left the Center and immigrated to Israel. Among them were Vabel Broder, Moshe Feldman, and others. A new administration was built in which the members participated: Zelig Mosman, Moshe Smolier, Yosef Wachbroit, Eliezer Basyuk, Yitzhak Wilner, Yosef Kligerman, and Yisrael Raznoshik.
The 7th conference that met in Warsaw, in which Mosman, Kligerman, and this author participated as representatives, argued bitterly over the direction and future of the movement. The report that was brought by the delegation heralded the beginning of the turning point. The pioneering movement whose wings were spread to the heavens - began to aim for the depths. The pioneer education for a life of honesty, justice, and good deeds came up against a harsh and bitter reality of daily life and the abundance of social and economic problems burdened the souls of the maturing youth.
Korets, this little city, suffered badly by being a border city. Dozens of villages that were the source of its livelihood were torn away and that left its mark on the economic and community life of the city. The youth especially suffered and their problems worsened day by day. Learn a profession? - Where? Work? Employment? - In what? Continuing education - with what resources?
[Page 224]
|
|
The Administration of the “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Center in 1929
Standing from right to left: 1) Yitzhak Wilner, 2) Dvora Garbasz, 3) Eliezer Basyuk, 4) Yosef Kligerman
Sitting from right to left: 1) Moshe Smolier, 2) Chaya Spielberg, 3) Yosef Wachbroit |
The Jewish family became impoverished and the characteristic occupations of the residents of the small towns - also due to the strengthening of anti-Semitism - became questionable. And how do we go forward? the members asked. The library that was on Synagogue Street - the spiritual center - no longer answered the question.
They began to leave the city, some to continuing education, some to training and immigration to Israel, and some to emigration elsewhere. The heads of the Center changed. Czudner, who was the head of the Center after Mezhyrichski immigrated to Israel, left for continuing education and Zelig Mosman was chosen in his place.
The author of this article, who took Mosman's place as the head of the Center, left the city in 1928 and Yosef Wachbroit was chosen as Center head. The ideological consolidation of the Center influenced its shape and changed its substance. Larger groups went out for training. The generation of the Bogrim immigrated to Israel or left the city. The young generation took over the leadership. Munya Góralnik, Mordechai Kagan, Sarah Szapiro, Yehezkel Weintuch, and others whose names I do not remember, sadly, left the Center. New young people entered the ranks and the chain continued until … the Holocaust and the bitter end.
[Page 225]
The Center and the Keren Kayemet[2]
The “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Center in Korets earned recognition not only by being the first and only youth movement in this city for many years, not just in serving as a school for hundreds of youth, where they studied and were educated towards their mission and their Zionist and socialist tasks, the Center also was a communal power of great influence over the communal and Zionist life in the city. Its part was great, in particular, in the work for the Keren Kayemet and it is not missing from the Keren Kayemet gold book [=list of donors]. Dr. Wallach (the treasurer of the Keren Kayemet), a venerable Zionist and dear Jew, accompanied from close up this widespread work. The blue box [=collection box for donations] was carried on the wings of this movement to every Jewish house. The United Jewish Appeal, the mail from the Keren Kayemet for the holidays, were the initiative and work of the Center. The work towards redemption of the land was an important part of the substance of its life.
If we could raise a monument over the grave of the holy ones in Korets that would be appropriate and would express the best of the ambitions and dreams of the local youth, and within it hundreds of young people, members of the “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Center - it would, without a doubt, be the blue box of the Keren Kayemet, a symbol of liberation, redemption, and the substance of its life.
The Center and the Branch of “Tarbut”
It was natural and obvious that the “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Center in Korets would make its mark on the development of communal and cultural life in the place. The “Tarbut” school, of which most of the members of the Center were students, was influenced by this movement. The members of the Center were, by nature, an organic part of the Hebrew culture movement in our city. They brought the Hebrew language out of the walls of the school and inserted it into the family home. They were among the first who spoke the Hebrew language in public. The Tsofim and the Bogrim of the Center gathered around the “Tarbut” library. The library on Synagogue Street was, seemingly, an organic part of this branch of the movement. The late member Blovstein, the veteran librarian, the devoted and true one, knew how to tell many interesting and characteristic things on this subject to the students of the Center.
The Center and Public Work
The “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Center struck deep roots in the community, not only in the area of culture. Its emissaries reached every corner of life in the Jewish community in the city. The leaders of the Center invested great effort in every Jewish undertaking that worked on behalf of the masses of the people. They participated in the “CENTOS” [=Jewish charity] and the “TAZ” [=daily newspaper], which were concerned with the health of the people, took care of orphans and children
[Page 226]
|
|
| The “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Club in Korets |
of poverty. It was natural and obvious that this movement would support every communal activity of a social nature that was concerned with the masses of the people.
This was what the “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir” Center was like during its existence. How was it at its end? Was it together with the people and did the people march their final steps with it? Did it rebel and rise up against the monster of the generation and not accept the decree of its elimination? This topic kept me busy for many years. It is possible that the lack of the distance in time required for accurate historical evaluation might influence incorrect views and thus my caution in giving an answer to the aforementioned question.
I will bring, therefore, facts and they will bear witness by themselves. Many of the students of the Center wrote a warning page in their own blood in the heroic struggle against the Nazi invader. Their hands were with the fighting partisan regiments that attacked German supplies for the front. Some of them joined the famous march of the partisan regiments under the leadership of Kovpak and, according to collected witness reports from collaborators, one can find along this entire route silent graves of Jewish heroes from among the youth of Korets, who fell with their weapons in their hands, in the hard and ugly struggle with the Germans. Only a few from among them were able to see the defeat of the enemy. Some of the fighting youth
[Page 227]
gathered around them isolated families looking for shelter in the forests and protected them. The long road in the forest killed most of them and only a few managed to go from slavery to freedom.
Some of the youth managed to join the ranks of the Red Army and marched with them from Stalingrad to Berlin. But the overwhelming majority of them, too, did not manage to participate in the day of victory.
But, the lion's share of the Center marched its last steps together with the entire Jewish community in the direction of the village of Kozak … in this grave is buried a generation that believed in mankind, that supported brotherhood, that aspired to a world of equality and justice. On the edge of this grave, all its dreams and aspirations vanished.
So was the Center in its final journey …
* * *
Translator's footnotes:
- A Zionist youth movement Return
- Jewish National Fund Return
[Page 228]
The “Gordonia” Federation in Korets
by Avraham Shilon (Gilman)
Translated by Monica Devens
“Gordonia” carries the name of Aharon-David Gordon, the pioneer of work and fulfillment, who immigrated to Israel when he was 48 - to realize the dream of his life. Over time, he became acclimatized to a life of work and became one of the pillars of the pioneers of the working settlement.
The movement in Poland, noting on its flag the slogan “Pioneering Zionism,” work, and fulfillment, was the source of the serious core groups for communal settlement in Israel.
As a boy, the cultivation of the political party, “Hitachdut” (in Israel - “Ha-Po'el Ha-Tza'ir”), whose viewpoints were identical to the idea of the movement, received, at the beginning of its journey in the twenties of our century, Zionist inspiration and faithful direction from the outstanding members of the party. In Korets, the members who were deserving of special esteem: Yisrael Melamed, Aharon Schenker, and Meir Gilman.
The pioneering-Zionist federation, “Gordonia,” operated with the help of two separate centers
|
|
The Leadership of “Gordonia”
Standing from right to left: 1) Tusya Solomianik. 2) Reuven Kipret. 3) Avraham Shilon. 4) Gecie Litvak. 5) Chana Zilberman
Sitting from right to left: 1) Yaakov Rubin. 2) Freyda Tsmolker. 3) Aizik Litvak. 4) Lyuba Melamed. 5) Mordechai Hendelman |
[Page 228]
in Poland, the Congress center and the Galician center. One was in Warsaw and the other - in Lviv. Branches were established in all the big cities and in the provincial towns, and one of the branches was in Korets.
The Organizational Structure
The institutions of leaders and guides were put together as the first leadership structure in Korets. At the head of the local leadership stood: Yaakov Rubin (head of the leadership), Freyda Tsmolker, Avraham Shilon (Gilman), Nachum Raznoshik, Reuven Kipret, and Gecie Litvak.
The first core group of the federation was organized out of the youth studying at the “Tarbut” school in the city. Afterwards young people from all the other elementary and high schools joined,
|
|
The “Gordonia” federation in 1933
First row (above) from right to left: 1) Mordechai Mutznik, 2) Yoel Góralnik. 3) Chaya Schneider, 4) Etel Shruba, 5) Shprintze Blinder, 6) Leah Shchigel. 7) Yehudit Markovetskiy, 8) Golda Garbasz, 9) Efraim Góralnik, 10) Chaim
Second row from right to left: 1) Miriam Becher, 2) Leah Konofit, 3) Sunya Krishtalik, 4) Góralnik, 5) Sarah Gorben, 6) Chaya Kristol, 7) Muzya Goltsman, 8) Nechama Anpolskiy, 9) Shimon Gilman
Third row from right to left: 1) Vaveh Vilner, 2) Yaakov Rubin, 3) Tusya Solomianik, 4) Yaakov Melamed, 5) Mumah Mabler, 6) Avraham Shilon (Shalin), 7) Gecie Litvak
Fourth row from right to left: 1) Motl Berman, 2) Pesia Shmuter, 3) Freydel Góralnik, 4) Taivel Rubin, 5) Chana Shalin, 6) Avraham Góralnik, 7) Grisha Kizman, 8) Yitzhak Chanin, 9) Aryeh Prikzania
Fifth Row: 1) Pulya Melamed, 2) Meir Litvak, 3) Itta Firkes, 4) Pesia Joresh, 5) Brash |
[Page 230]
bringing the number to 150-200 young people. With the growth of the federation, the young members separated off from the older ones and there became two age groups: the young, “Ha- Tzofim,” and the older took the name, “Magshimim.” The age groups divided into small groups at the head of which stood a responsible member - group head. These group heads became the local council to which members were elected: Yehoshua Basyuk (group head) and the heads of the groups: Rivka Firkes, Batsheva and Mizya Markus, Alta Melamed, Yisrael Fromin, Bluma Fuchs, Zev Vilner, Tusya Solomianik, Meir and Aizik Litvak, Ahuva Melamed, Mordechai Basyuk, Yitzhak Schorin, Luba Shmuter, Mordechai Barzov, Sprintze Blinder, and with the active participation of the member Hendelman (school teacher), Mumah Mabler, and the member Edla Lidski.
Organizational-Cultural Activity
The basic level of the federation of the young students received a scouting-sportive education that included: calisthenics, hikes, summer camps, creation of special entertainment experiences, which drew the youth to social life and working as a group through an integration of cultural activity and explanation of the basic principles of Zionism, “He-Halutz” and the movement, and also illustrating the explanation through their participation by helping the adults with all the activities of the movement, in the area of pioneering and in the national funds - “Keren Kayemet” and “Keren Ha-Yesod.” These activities were designed to awaken in the youth the desire to develop from birth their independent initiative and their talents.
The Magshimim
The older level in the federation was different from its sister in structure and in education. The activities of organization and culture in this level were based, principally, on individual fulfillment through active participation of the members in activities of the national funds and other communal work. These members listened to serious lectures about the Zionist movement, about the Jewish people (from both a historical and a geographical perspective), and about settlement in Israel.
Most of these members went on later to groups of pioneering training, which existed in Poland for training core groups to immigrate to Israel. At the training places, they trained themselves for physical work and collective living in preparation for their integration into working settlements in Israel. This was an interesting period in the life of a young person who left
[Page 231]
|
|
The “Gordonia” Branch Before the Outbreak of the Second World War
First row (above) from right to left: 1) Tzirel Schneider. 2) Golda Segal. 3) Fajgowt. 4) Fajgowt. 5) Berel Finkleman. 6) Ben-Zion Anopolskiy, 7) Pinchas Geshel, 8) Noach Kleinfeld, 9) Yaakov Smolier, 10) Nunya Skletzky, 11) Yitzhak Firkes, 12) Firkes, 13) Yaakov Frimerman, 14, 15) , 16) Yaakov Raznoshik, 17) Vaveh Barzov
Second row: 1) Chava Gurvand, 2) Reva Karolinski, 3) Abba Hirsch, 4) Bluma Neiterman, 5) Zvi Molier, 6) Motl Firkes, 7) Yoel Kunicher, 8) Beila Neiterman, 9)
Third row: 1) Kunicher, 2) Shmuel Finkleman, 3) Chasia Yaronsky, 4) Vilentsik, 5) Mal, 6) Faiga Bernstein, 7) Hasya Beren, 8) Perlman, 9) Dutzi Vilner, 10) Mordechai Blovstein
Fourth row: 1) Reva Aberbuch, 2) Dutzi Frimerman, 3) Chaya Bardach, 4) Mitzik Schorin, 5) Kunicher, 6) Perel Kligstein, 7) Bracha Adler, 8) Doba Neiterman |
[Page 232]
his home and his parents and became overnight a person who ruled over himself, but it was also a test of the degree of his rooting in the designated country and the degree of his acclimation to the new life in the working settlement. These youth did not disappoint us.
In Israel, he joined the communal settlement and added important, vigorous pioneering strength, awake to everything that was being done and was happening in Israel. Are they not, in fact, the core groups that we meet today, firmly established in the soil of the homeland and continuing along the basic lines that the teacher and illustrious pioneer, Aharon-David Gordon, outlined.
* * *
[Page 233]
From “Hovevei Sfat-Ever” to “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir”
by Noach Dagoni
Translated by Monica Devens
In 1928, I raised the idea among a small group of young people to establish a club for Zionist action. We were 14-15 years old then, graduates of the “Tarbut” school. In order to continue our education, it was necessary to go to Rovno [=Rivne] because there was no Hebrew High School in Korets. The economic conditions that permitted continuing education were available to only a very few. Even learning a profession wasn't there.
Upon finishing the “Tarbut” elementary school, we felt that a certain chapter of our lives had come to an end, but the future was vague and unclear. We were afraid that an empty shell was foreseen for us.
Korets was poor and downtrodden, without sources of livelihood. Economic possibilities were limited and so its residents lived a gray and trouble-filled life and the youth knew that there was no chance to change the situation unless a miracle occurred. The house, the general atmosphere, enforced idleness, the vague day after tomorrow - created a kind of incubator growing boredom and emptiness.
|
|
The Founders of the “Hovevei Sfat-Ever” Federation
Standing from right to left: 1) Zvi Ferchik, 2) Noach Dagoni (Hecht), 3) Nachman Gilgon, 4) Boris Hirschenhorn, 5) Mordechai Turchinskij, 6) Yitzhak Chanin, 7) Aryeh Prikzania
Sitting from right to left: 1) Lyuba Vilner, 2) Yosef Broder, 3) Mordechai Basyuk, 4) Dov Gutnik |
[Page 234]
The young people felt like the ground was falling out from under them. There was nowhere to flee to so they sought a way to initiate something against the gray and withered reality.
The appearance of the ideological shades and streams in Zionism opened broad horizons for the youth of Korets. It was as if the youth waited for this moment. The alert and active part of them established Zionist youth federations.
At this period, “Ha-Shomer Ha-Tza'ir,” “Gordonia,” and “Freiheit” already existed in Korets. However, for one reason or another, they did not draw us in. We decided, therefore, to organize as a separate federation and we set before ourselves the goal of spreading the Hebrew language and activity on behalf of the Land of Israel.
The founders were, in [Hebrew] alphabetical order: Mordechai Basyuk, Yosef Broder, Dov Gutnik, Nachman (Munya) Gilgon, Boris Hirschenhorn, Aryeh Vilner, Yitzhak Chanin, Mordechai Turchinskij, Leibush Prikzania, Zvi Ferchik, Chaim Shostak, and the author of this article. Later on, Pesia Joresh and Mina Mabler joined us.
Since the heart of our goal was spreading the Hebrew language, we emphasized this mission by choosing the name, “Agudat Hovevei Sfat-Ever” [=Association of Lovers of the Hebrew Language].
The outstanding teacher and educator, Mr. David Solomianik, of whom the great majority of us were students - supported us and helped us right from the beginning.
Most of the young people were already organized in the existing Zionist youth movements and so we invested a lot of effort into drawing young people to our association from among the school students. We knew that, in order to do this, we required a hall (or “clubhouse,” in the terminology of those days) that would serve as a meeting place in the evenings in order to carry out cultural work and spend pleasant time together. However, for that we needed money, which was not to be found in our pockets, because most of us were still dependent on our parents. It was obvious that it was impossible to request money from the parents for this goal.
We were young. The blood boiled, desire burned, imagination blossomed, and it seemed to us that there was no limit to our ability. And so, this mighty desire gave birth to actions that seemed then to many strange and surprising. Some of us who gave private lessons and earned about 15 gold coins a month gave our money and, with this money, we opened a club in Yosef Zaltzman's mother's house. This wasn't a particularly large hall, but to our eyes, it was perfection and the height of achievements.
We gathered together in the evenings, sang, read, listened to lectures, and enjoyed time together. We were thirsty for action. The first action was the decision concerning the obligation to speak Hebrew among ourselves, at home, and in the street. This decision led, at times, to ridiculous situations when we refused to answer people who spoke to us in Yiddish. The consistent stubbornness, however, did not change the situation in the street,
[Page 235]
|
|
The “Hovevei Sfat-Ever” Association
First row (above) from right to left: 1) Bracha Zweig, 2) Lyuba Vilner, 3) Moshe Reif, 4) Vaveh Vilner
Second row: 1) Faiga Kaminstein, 2) Chayke Rimerman, 3) Fredka Witman, 4) Mina Mabler, 5) Chaim-Yosef Shostak, 6) Noach Dagoni, 7) Motl Mutznik, 8) Mordechai Turchinskij, 9) Nunya Tsipinskiy, 10) Hirschel Tsipinskiy
Third row: 1) Fishman, 2) Esther Turchinskij, 3) Dov Gutnik, 4) Zvi Ferchik, 5) Yitzhak Chanin
Fourth row: 1) Lyuba Reif, 2) Yosef Broder, 3) Munya Gilgon, 4) Dov Buf, 5) Reva Breindes, 6) Mordechai Basyuk, 7) Pesach Yaronsky
Fifth row: 1) Masya Breindes, 2) Sarah Polichuk, 3) Sarah Fajgowt, 4) Chaya Chichki, 5) Baba Goldberg, 6) Moshe Finer (visitor from Israel), 7) Yeshayahu Serota, 8) Lyuba Firkes
Sixth row: 1) Nechama Herschenhorn, 2) Pesia Joresh, 3) Dutzia Witman, 4) Raya Shmulson, 5) Chayke Kutsher, 6) Manya Geifman, 7) Mizya Wilner, 8) Pola Melamed |
but got many people used to seeing in us Don Quixotes and to become okay with it. The second was the activity on behalf of the Keren Kayemet [=Jewish National Fund]. We asked them to let us join the group of activists, but the youth federations opposed it because our association was not honest in their eyes. Let us remember for good the legacy of Mr. Herzl Zilberman of the Keren Kayemet who took our side and brought us in to the activity.
We dedicated ourselves to the activity on behalf of the Keren Kayemet with great vigor and with the fire of youth. We wanted to prove that, although we were few in number, hidden within us was great and praiseworthy ability. And, in fact, within only a short time, we reached second place in the list of outstanding fund raisers.
Our publicity that we carried out principally among the school youth - drew many of them
[Page 236]
to our association. Even those who had finished “public education,” students who didn't know Hebrew, joined us and they organized in the club courses to acquire the language.
Youngsters between the ages of 10 and 12 were organized into the levels of the young ones. In a short time, the number of members of the association reached 60 youngsters.
The pamphlet, that appeared during three consecutive years, claimed an honored place among the cultural work. In the first year, it appeared as a weekly - in the second, as a monthly - and in the third, as a wall newspaper. This pamphlet, even if today it appears to us as an unripe fruit of the mischief of youth was, in its time, an important journal that united most of the members of the association.[1]
The cultural activists in the association were Mordechai Basyuk, Aryeh Prikzania (who particularly excelled in writing), Pesia Joresh, Lyuba Firkes, Freyda Goralnik, and Fredka Witman.
The Land of Israel - the content and goal of our education - was something that was for us, in its simplest form, a distant dream that could not be integrated, as it were, into the framework of our existence. The appearance of a newspaper or a book from the Land of Israel was a great celebration for us. We didn't just read it, but we studied it and we learned its content by heart. We weren't yet familiar with ideological ways and political shades so everything from which the smell of the Land of Israel wafted - perfumed us. The coming of a Koretser from the Land of Israel was an event for us. We didn't investigate who the person was or what he did in Israel. The fact that he was “Israeli” crowned him with an awe-inspiring halo. We invited him so that we could hear directly from him what was happening in Israel, we took photos with him, and we surrounded him like Hasids with their rebbe.
Reality taught us that an organization needed accessories, like a membership certificate, seal, announcements in the hall, etc. And if there were only these external things - their influence on the youngsters was very noticeable.
With the increase in the number of members, the financial burden eased somewhat. We moved to another clubhouse, with 2 rooms, we decorated it with maps of the Land of Israel, announcements, and posters, and we turned it into a warm corner where the youngsters found an alternative to the angry and grief-filled home.
The cultural activity broadened and flourished. About 200 books were acquired and a lending library for the members of the association opened. We organized parties where the young levels presented various plays to whose performances the parents were also invited.
We felt that we were leading the youth down the correct path towards personal development.
The riots of 1929 were for us a hard blow and heavy turmoil. From these riots, we learned that the reality in Israel required every person to know how to protect his life with weapons. We started to look for ways to learn self-defense. Many of us signed up with the military training association
[Page 237]
[Page 238]
(P.W.) in order to learn how to use a weapon in an emergency and even though the army guides were anti-Semitic and their attitude towards us was not particularly friendly - we still encouraged our members to sign up and train.
The activity continued like this for three years - until 1931.
“He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” [=a Zionist youth movement]
Years passed, we grew up, our ideas deepened, and we became aware that education only in speaking Hebrew, without any connection to a particular movement - had no grip in reality. We were also placed in front of the personal fulfillment problem, the meaning of which was immigration to Israel. This matter required being affiliated with a pioneering-Zionist movement.
The fact that Korets was a frontier city, only about a half kilometer from the Soviet border, and that there was a constant curfew from 10 in the evening until 6 in the morning, served as an additional reason. In a reality like this, it would not be possible for a club to exist without a government license. And, in fact, more than once the authorities checked the clubhouse of “Agudat Hovevei Sfat-Ever” to clarify to which movement it belonged. It was clear to us that we would not be able to exist for a long time without permission from the authorities.
An unending agitation of ideas and arguments began among us about the question, what is the closest movement to us from the perspective of ideas. We invited lecturers from different movements to tell us the ideological basis of their movement. After arguments and clarifications that lasted for several months, it seemed to us that the “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” movement that espoused emigration, fulfillment, and education for the general group, was closest. We decided to find out the conditions of connection with the “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” movement.
For this purpose, they sent Mordechai Turchinskij and the author of this article to the district committee of the Volhynia region that was in Rovno [=Rivne] in order to clarify all the problems connected with this affliation.[2]
They spent two days in Rovno [=Rivne] and, after receiving explanations and instructions, they returned with the clear decision of joining the “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” movement.
At the general meeting, the two emissaries gave a report and it was decided by majority vote
[Page 239]
|
|
Standing from right to left: 1) Michael Kleiner, 2) Lyuba Litvak, 3) Nachman Gilgon, 4) , 5) Meir Kahana, 6) Zev Litvak, 7) Chaim-Yosef Shostak
Sitting from right to left: 1) Reva Breindes, 2) Chaya , 3) Noach Dagoni (Hecht), 4) Perel Geifman, 5) Reva Bliman
Sitting below from right to left: 1) Baruch Narbus, 2) Yitzhak Dagoni (Hecht), 3) Vilner, 4) Linik, 5) Neta Goldman |
that “Agudat Hovevei Sfat-Ever” would join “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir.” A small minority opposed this and supported continuing to exist separately. (Among the most strident opponents to joining “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” were: Dov Gutnik, Pesia Joresh, Ferchik, and Mordechai Basyuk). They supported an independent existence of the association. A dispute broke out. The minority continued with its independent existence for a short time until it fell apart. Some of its members joined “Beitar,” which was established then in Korets, and others joined other movements.
A committee was created made up of the members: Mordechai Turchinskij, Nachman Gilgon, and the author of this article. We rented a large clubhouse, decorated it, built a “ping pong” table, which was kind of a sensation in the city because this was the first one. “Ping pong” drew a lot of young people to the clubhouse who paid to play and we paid the rent on the clubhouse from this income.
Education for manual labor, which most of us were not used to, pushed us to organize a kind of training group. We looked for places to work. Many ridiculed us. A few were nice. The group found work, which was accepted at that period throughout Volhynia as outstanding training work, which was: cutting trees. We got
[Page 240]
a number of contracts to cut trees, principally for Kagan. The pay was minimal, the output small because we weren't accustomed to the work. Still, our spirits were at their highest. We worked with great energy. The salary was dedicated to maintaining the clubhouse. When our parents learned about it, they were outraged, but over time they got used to it and calmed down because they saw in this only youthful follies.
The “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” center sent us information that made it easier for the guides to fix and prepare lecture topics for the branch. We developed diverse cultural activities. We organized joint gatherings with the “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” branch in Mezhyrichi under the leadership of the member, Shulke Taytsher. Under cover of the “He-Halutz” [=the parallel Zionist movement for older youth] license, we arranged full-day hikes to forests in the area. The members of the branch felt that new horizons had opened up in front of them. Many of them were sent to summer camps for guides and, with their return, the blessed work was strengthened.
The author of this article was chosen as the “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” representative on the Keren Kayemet [=Jewish National Fund] committee in the city and also on the “He-Halutz” committee and was afterwards its secretary, which permitted coordination between the two federations regarding joint activities.
In 1931, with a festive ceremony, we transferred the first graduates of “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” to “He-Halutz.” These members did not leave the place that shaped them and continued to work and to direct “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir.”
In 1932, I went out for training. At that time, the branch had about 60 members. The educational activity was organized in 4 levels of “Tze'irim” and “Drorim.” The level of young guides grew and were prepared to bear the burden.
A new committee was chosen made up of the members: Yitzhak Hecht (now Dagoni), Nachman Gilgon, Chaim Shostak, Zev Litvak, and Dov Buf. Mordechai Turchinskij, who was already in “He-Halutz,” helped with the leadership.
The new committee began its activities with great momentum. It participated in an activity on behalf of the Keren Kayemet, distributing shekels, helping the block of the Land of Israel working towards the Congress and also continuing to send members to summer camps. Zev Litvak, Reznick, and Vilner went to the regional seminar.
A training company of the Klosova [=Klesiv] block was organized in Korets that year. A number of people who had come out of “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” were found in this training company, including Bat-Zion Shoshani-Turtcheniok. Bat-Zion considered it a delightful obligation to participate in the training company of “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” in Korets. This company injected a new spirit into the branch. Reciprocity developed: the company helped the branch and the branch helped the training company get work.
[Page 241]
In 1934, the “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” center became legalized with the name “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir,” which saw fear of the authorities depart. Until then, activity was sometimes cut off due to the constant searching to find shelter under the wings of the license of one party or another. Now, upon receiving the license, the possibility existed to bring lecturers for the cultural activities in the branch. We rented a hall together with the “Vitkinia” federation that was established that year in Korets.
On Adar 11 of that year [=February 26, 1934], in the “Sokol” hall, a joint academy of “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” and “He-Halutz” was held. Members of the branch participated in presenting local photos and a choir of the young levels also appeared. All of the income was designated for the “He-Halutz” fund.
In 1935, Yitzhak Dagoni (Hecht) organized, through “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir,” a sports division that later got the name “Ha-Po'el.” With great difficulty, one penny was added to another in order to acquire a soccer ball and net. Nevertheless, after this, a widespread sports division developed.
On January 15, 1937, Korets became Strefa Graniczna [=border zone]. The entire governance was turned over to the army. The Starosta left the city. It was forbidden to be in the street from 8 in the evening until 6 in the morning. Anyone who violated the law was fined 25 zlotys, which had to be paid to the army on the spot. This matter cut off the activities of all the youth federations almost entirely.
The young people started to scatter and anyone who had the opportunity fled the city.
A large part of the graduates of “He-Halutz Ha-Tza'ir” went for training and many of them succeeded and emigrated to Israel. On the eve of the war breaking out, however, the large majority, and especially the young people, were left in the city.
This situation continued until 1939.
With the Soviet conquest of Korets, all the Zionist youth movements scattered.
Under Soviet rule, possibilities for study and sources of work opened up for young people. The young people of Korets, thirsty for work and study, surged to this source in a mighty stream, but the entry of Nazi Germany into Poland put an end to this thirst quenching. Many of the young people were drafted into the Red Army and some of them fell in the battles of this army.
Some fled to the forests and fought with the partisans. Many fell in those battles. A few managed to survive in the wilds of Russia. Of those, some emigrated to Israel and a few are spread around the other countries.
But the majority of the members of the branch were annihilated by the Nazi enemy.
Thus the end came to one of the many pioneering youth movements in the city of Korets in the corner of Volhynia.
Original footnotes:
- I have kept these pamphlets to this day. Return
- These two emissaries went to Rovno [=Rivne] on foot because there was no money to pay for travel expenses. It was winter, snow covered the roads, and they got as far as Hoshcha with difficulty. From there, they traveled by “tremp” [=hitchhiking] with a farmer to Rovno [=Rivne], almost frozen in the cold. Return
[Page 242]
The Z. S. Youth and “Freiheit”
by Avraham Gilgon
Translated by Monica Devens
The “Z. S. [=Socialist Zionists] Tze'irei Tziyon” party began to organize a youth movement out of fear and concern for its future. The first core group of this movement began to sprout in 1921-22. In the beginning, it did not yet carry the name “Freiheit,” but rather Z. S. Youth. The first clubhouse opened in the home of Yisrael-Wolf Gutnik on Munstirska Street.
The first ones were a group of students aged 15-16, numbering about 15 people, and it existed as a closed group for almost two years. The educational work was organized around two principal topics: the doctrine of Zionism and the doctrine of Socialism.
The organizers of these young people were Moshe Bliman (Hadas) and Asher Shikher. This group was made up entirely of young girls. I was the one and only boy. Of the girls of the group, I remember the names of Gensia Freidis, Chenia Markus, and Sonya Yatum.
At a later period, a fundamental change began in the human make-up. True to the general line of the party that it was to be a party of the masses, we opened the doors to the youth of “Amcha” [=average people]. We began to include the youth of the working classes and the poor, the children of workers and the “small class,” who were far removed from matters of Zionism and Israel. However, when the movement took on a popular nature - the students and the educated left the group.
|
|
The leadership of “Jugend-Freiheit”
Standing from right to left: 1) Chaim Zuker, 2) Aharon Yerushalimsky, 3) Avraham Gilgon, 4) Yaakov Pava
Sitting from right to left: 1) Chaya Brik, 2) Chana Grinfeld, 3) Bracha Shtilerman |
[Page 243]
|
|
“Freiheit” Youth
First row (above), standing from right to left: 1) Michael Polichuk, 2) Pinchas Kleiner, 3) Mendel Oberstern, 4) Gecie Milrod, 5) Mordechai Torknitsch
Second row: 1) Avraham Nudler, 2) Yitzhak, 3) Yitzhak Mutznik, 4) David Sandler, 5) Avraham Brautman, 6) Shlomo Ozerinsky, 7) Mordechai Kleiner
Third row: 1) Gedaliah Shukhman, 2) Avraham Anopolskiy, 3) Asher Góralnik, 4) Chaim Zuker, 5) Yehoshua Glis, 6) A. Rozendorn, 7) M. Gilshlak, 8) M. Milrod
Fourth row: 1) Chana Grinfeld, 2) Dov Bernstein, 3) Yitzhak Schocken, 4) Nachum Waserszturm, 5) Bracha Shtilerman
Fifth row: 1) Susil Kagan, 2) Etel Linik, 3) Freydel Linik, 4) Leah'le Fabrikant, 5) Chasia Kuperstein, 6) Freydel Peres, 7) Golda Chamra, 8) Moshe Schneiderman
Sixth row: 1) Menachem Goldstein, 2) Etel Schneiderman, 3) Golda Barak, 4) Lyuba Firkes, 5) Chaya Brik, 6) Sheva Neiterman, 7) Tzippora Linik, 8) Shlomo Shikher |
[Page 244]
The knowledge that Aharon Yeruzlimski, the son of R. Leizerl, had joined the Z. S. Youth hit like thunder on a bright day. This young man suffered considerably from the strict religious regime in the house of his father, the Rav. Thus it came to “a revolutionary change.” He began to cut down trees and joined a movement whose atmosphere was the complete opposite of that of his parents' house. In this there was a sign of the great discontent that surrounded the Jewish youth of Korets, which got the name in the literature of “change of values” and which Borochov defined with this, that the Judaism that was positioned in the head, in longwinded debate, in matters of heaven, we must instead position it on the group and create an earthly Judaism that draws its vitality from the soil. The Z. S. Youth filled this task of giving a socialist form to the lives of the youth of Korets through deep and continuous educational activities.
In 1926, Z. S. Youth was the live topic of the party. We included ourselves in activities on behalf of Keren Kayemet [=Jewish National Fund], Kapai [=Land of Israel Workers Fund], and other Zionist fundraising appeals. All of our actions were directed toward preparing the youth for “pioneering” and for emigration to the Land of Israel. The Z. S. Youth did not disappoint and many of us fulfilled the dream and emigrated to Israel.
The Zionist work of the Z. S. Youth was well recognized within the Jewish populace in Korets. If, in 1926, the Z. S. party succeeded in getting a third of all the members of the city council, this was due principally to the great energy that the members of Z. S. Youth, who then numbered 200 members, one of the strongest branches in all of Volhynia, invested.
The educational activities of Z. S. Youth expressed themselves in acquiring Zionist and Socialist values. We also organized a library that served the youth.
In 1926, we stopped calling ourselves Z. S. Youth and took on the name “Freiheit.” The initiative to organize youth up to age 14 came from us. We organized it and called these groups “Jugend-Freiheit.” The first guides of these young people were Bracha Shtilerman, Grinfeld, Brik, and Zuker. Dov Bernstein, one of the activists of the Z. S. party who helped a lot in the development of this movement, joined them later.
Even after I emigrated to Israel, as did other activists, the movement continued to spread and to bring to the Zionist labor movement many young people who were far from it. The Zionist and Hebrew activity deepened its roots and, with every wave of immigration coming from Korets to Israel, there were represented in it pioneers whose first socialist and Zionist education was received in the “Freiheit” movement.
[Page 245]
“Ha-Po'el Ha-Mizrachi”
by Daniel Bernstein
Translated by Monica Devens
The “Ha-Po'el Ha-Mizrachi” party was not one of the large and outstanding ones in our city. In its entirety, it counted a few tens of religious young men. Nevertheless, because of the difference and the specialness of it, it is fitting that this party appears in this book.
The first shoots of “Ha-Po'el Ha-Mizrachi” appeared in 1922. Its founders were: Herzl Zilberman, Ha-Rav Yitzhak Yeruzlimski, Yaakov Gosher, and the author of this article.
In Korets, there were suitable conditions and facts for the establishment of a religious party. The large “Yeshiva” served as the basis and the principal source of the human capital. The founders of the party offered the logical, in my opinion, hypothesis that the great majority of the students of the “Yeshiva” would join “Ha-Po'el Ha-Mizrachi.” The activists, of whom part were students of the “Yeshiva,” examined the young men who were studying and became aware that the flame of the Zionist idea had begun in their hearts. And, in fact, some of them were swept away by the vision of national revival and were very active in the Zionist sector.
The “Yeshiva” did not disappoint from this point of view. The party got to be 50 members who assembled at Ha-Rav Yeruzlimski's house. It developed nicely and took its place in the Zionist movement in our city. The committee and the party members took an active part in distributing shekels, and in particular with the funds. The chairman of the party, Herzl Zilberman, presented the party as authorized by the Keren Kayemet and he was praised and lauded in the city for his devoted work on behalf of this fund.
Over time, other activist members joined the party, among them: Yehuda Feiner, Zvi Eisenberg, Brandwein, Leibl Goldman (today a rabbi in Boston), and Yeshaya Serota (living in Israel).
The party organized Torah study lessons, which took place twice a week. Similarly, they would gather for elucidation and clarification of the ideology of religious Zionism.
To my sorrow, and that of us all, the great majority were lost in the Holocaust.
This material is made available by JewishGen, Inc.
and the Yizkor Book Project for the purpose of
fulfilling our
mission of disseminating information about the Holocaust and
destroyed Jewish communities.
This material may not be copied,
sold or bartered without JewishGen, Inc.'s permission. Rights may be
reserved by the copyright holder.
JewishGen, Inc. makes no representations regarding the accuracy of
the translation. The reader may wish to refer to the original material
for verification.
JewishGen is not responsible for inaccuracies or omissions in the original work and cannot rewrite or edit the text to correct inaccuracies and/or omissions.
Our mission is to produce a translation of the original work and we cannot verify the accuracy of statements or alter facts cited.
 Korets, Ukraine
Korets, Ukraine
 Yizkor Book Project
Yizkor Book Project
 JewishGen Home Page
JewishGen Home Page
Yizkor Book Director, Lance Ackerfeld
This web page created by Lance Ackerfeld
Copyright © 1999-2025 by JewishGen, Inc.
Updated 03 Dec 2024 by JH